Lasik Surgery - Vision Care Glossary
Glossary of Lasik Surgery Medical Terms
Home > Lasik Surgery > Vision Care GlossaryAstigmatism
Astigmatism is blurry vision produced by football-shaped corneas, which are too steep in one place and too flat in another. Astigmatic corneas focus light in two different places in the eye, making both near and distance vision a problem.
Best corrected visual acuity (BCVA)
The best possible vision a person can achieve with corrective lenses measured in terms of Snellen lines on an eye chart.
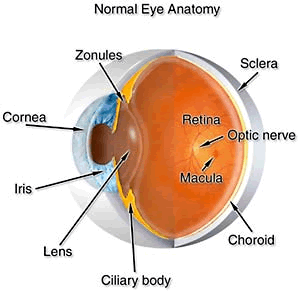
Cornea
The transparent front segment of the eye that covers the iris, pupil and anterior chamber, providing most of the eye's optical power. This is the part of the eye reshaped by laser vision correction.
Diopter
A measurement of the degree to which light converges or diverges; also a measurement of lens refractive power.
'The Fingerprint of Your Vision'
Because no two eyes are alike, each eye has a unique map, or fingerprint. 'The Fingerprint of Your Vision' defines unique characteristics in each individual's vision, which are measured by WaveScan technology.
Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
Also known as farsightedness, is a refractive error in which you see better from a distance than close up. Hyperopia is caused by an eyeball that is too short to focus light on the retina. Light strikes the retina before it can come to a sharp focus.
Myopia (Nearsightedness)
Also known as nearsightedness, is a refractive error in which you see better close up than from a distance. Myopia is caused by an eyeball that is too long to focus light on the retina or a cornea, which is too steeply curved. In these cases light focuses in front of the retina rather than on it.
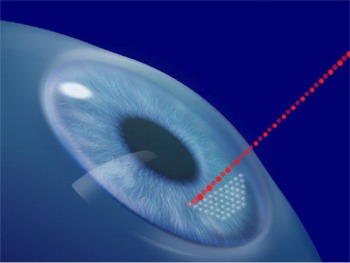
Refractive Surgery
The role of refractive surgery is to reshape the surface of the cornea, which is the clear dome over your iris. Your cornea provides a majority of the focusing power for the eye. It does this by way of directing light through your natural lens, located in the center of your pupil behind the iris. This lens is then able to fine-tune your focus of vision. The light then shines through onto the retina of the eye. The retina then transmits the image to the brain to produce vision.
Retina
The thin lining at the back of the eye that converts images from the eye's optical system into electronic impulses sent along the optic nerve for transmission to the brain.
Snellen Chart
The chart used to test visual acuity with black letters of various sizes against a white background.
Uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA)
The best possible vision a person can achieve without corrective lenses measured in terms of Snellen lines on an eye chart.